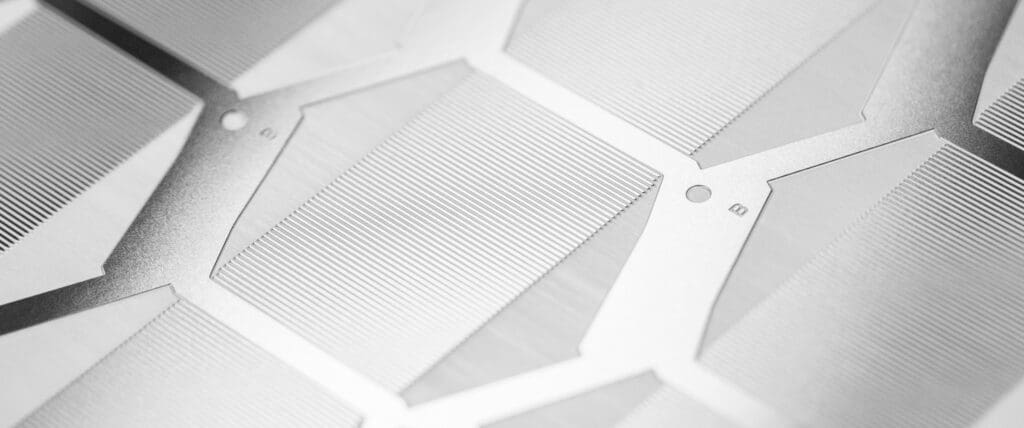
Understanding printed circuit heat exchangers & the role of chemical etching
Printed circuit heat exchangers (PCHEs) are specialist plate heat exchangers which facilitate the efficient transfer of heat between two fluids. In this article, we explore what printed heat exchangers are, and how Precision Micro’s industry leading chemical etching service is the enabling solution for their production.
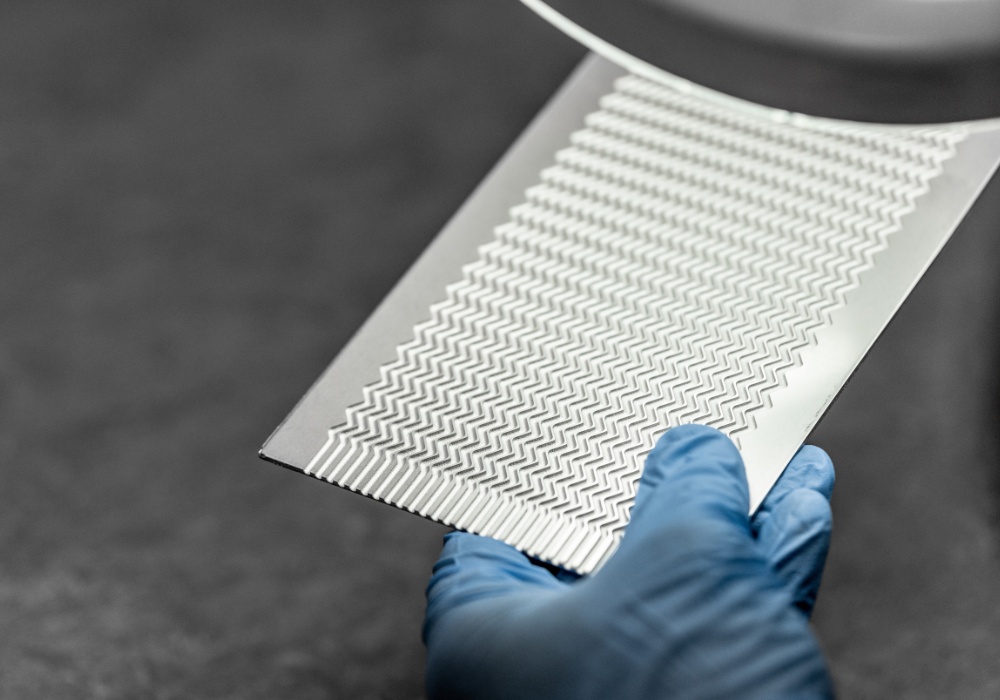
What is a printed circuit heat exchanger?
Printed circuit heat exchangers (PCHEs) are specifically manufactured to optimise thermal energy exchange between two fluids. These devices combine the technologies of chemical etching and diffusion bonding. Flow channels are etched onto metal plates, which are then stacked and solid-state joined to create a unified block.
What are the advantages of printed circuit heat exchangers?
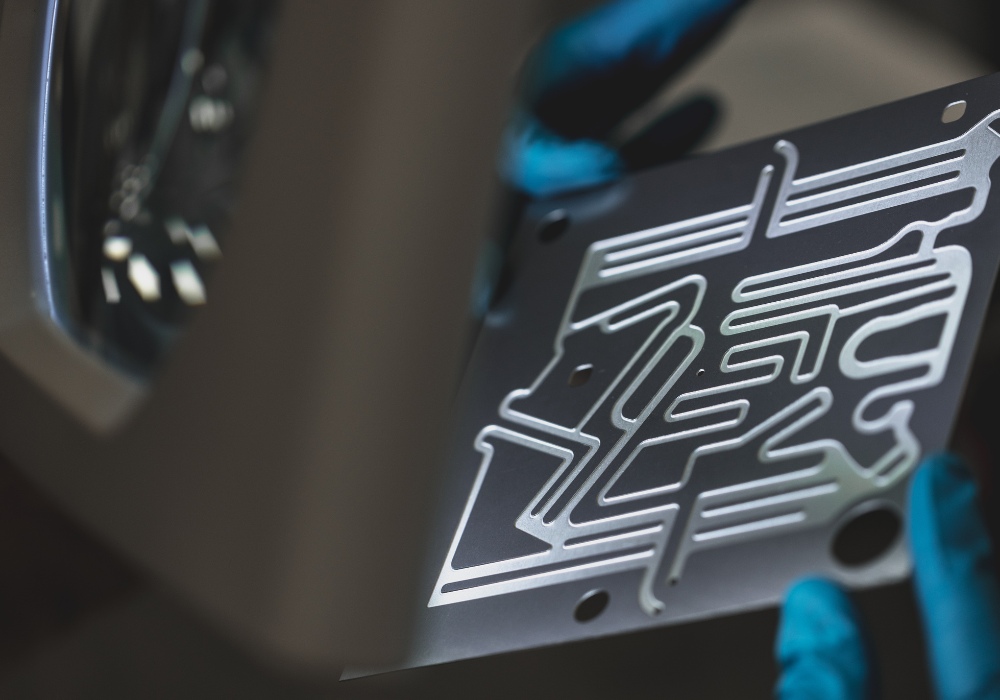 Printed circuit heat exchangers offer engineers compact designs, ensuring efficient heat transfer and high thermal performance through intricate flow patterns. The precise geometries of PCHE channels also enhance thermal management and efficiency by creating large surface areas for effective heat transfer between fluids. With exceptional high-pressure tolerance, they are ideal for industrial processes under elevated pressures. Additionally, their lower fluid inventory compared to conventional exchangers enhances heat transfer performance and reliability.
Printed circuit heat exchangers offer engineers compact designs, ensuring efficient heat transfer and high thermal performance through intricate flow patterns. The precise geometries of PCHE channels also enhance thermal management and efficiency by creating large surface areas for effective heat transfer between fluids. With exceptional high-pressure tolerance, they are ideal for industrial processes under elevated pressures. Additionally, their lower fluid inventory compared to conventional exchangers enhances heat transfer performance and reliability.
Printed circuit heat exchanger applications
The efficiency of diffusion bonded heat exchangers makes them valuable in a range of applications, including the cooling and liquefaction of natural gas, precooling of hydrogen in hydrogen refuelling applications and carbon capture in the renewable energies sector.
Appropriate materials for printed circuit heat exchangers
Due to the nature of their application, PCHEs are typically made from metals with high thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. Stainless steel stands out as the most common material choice, favoured for its low cost, corrosion resistance, durability and versatile properties. Grades such as 304 and 316 are typically utilised in their production.
As chemical etching technology is suitable for almost any metal type up to 2.5mm thick, PCHE flow plates can also be manufactured using nickel and copper alloys, aluminium and other specialist metal types or grades.
How chemical etching optimises the production of printed circuit heat exchangers
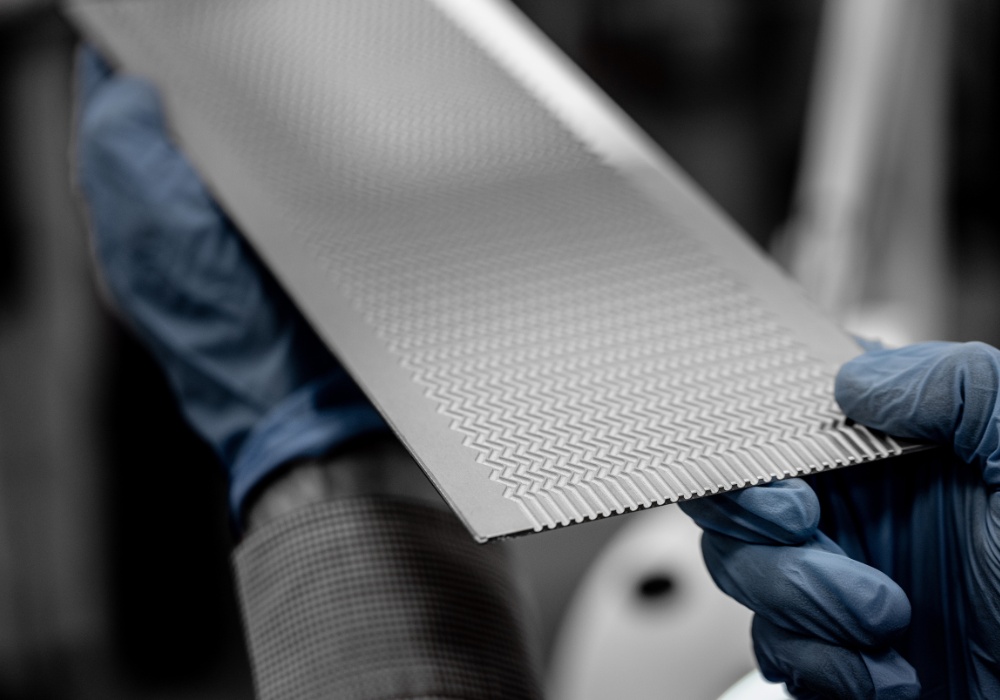
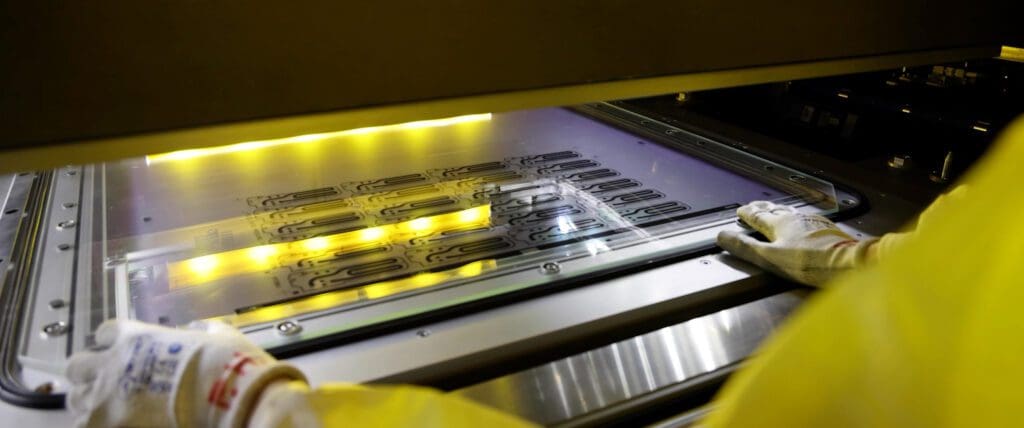
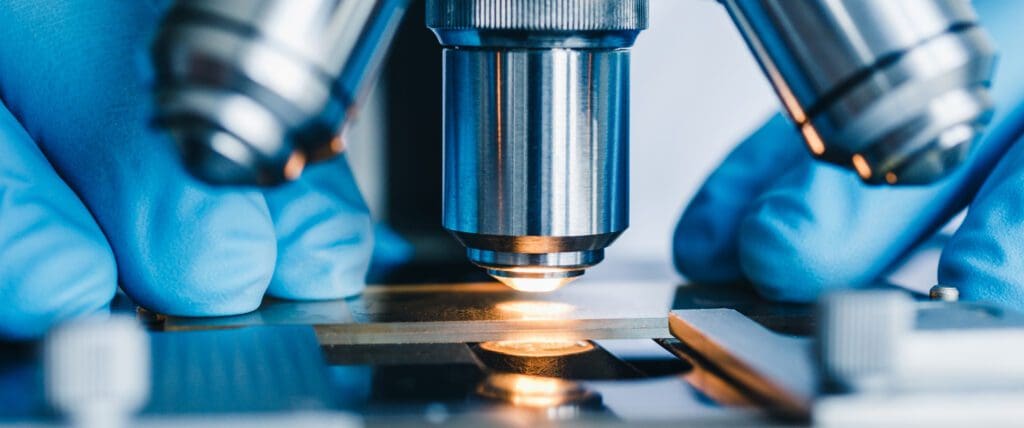
Photochemical etching serves as an enabling solution for producing PCHEs, with chemical etchants used to selectively dissolve intricate patterns and flow channels onto a metal sheet.
Unlike conventional sheet metal machining techniques, chemical etching maintains the properties of sheet metals and prevents the risk of material distortion by employing a chemical reaction to selectively dissolve material from a metal sheet. This ensures optimal part performance, as opposed to using stamping, which can cause cutting-edge stress, negatively impacting the overall performance of the diffusion bonded heat exchanger.
Cost-efficient tooling and accelerated production
Photo etching eliminates the necessity for costly hard tooling by utilising digital tooling, serving as a cost-effective alternative. Digital tooling streamlines the requirement for costly tooling adaptation, ensuring that designs are optimised at a fixed, economic cost. Furthermore, lead times are accelerated with prototyping available in as little as a few days, enhancing the time-to-market.
Process versatility
The photochemical etching process provides engineers with volume flexibility by accommodating prototyping to the large-scale production of printed circuit heat exchangers. Moreover, etching can handle larger and thicker sheets and facilitates a broader range of metals, which would present challenges when processed through traditional machining methods.
Intricate flow channels
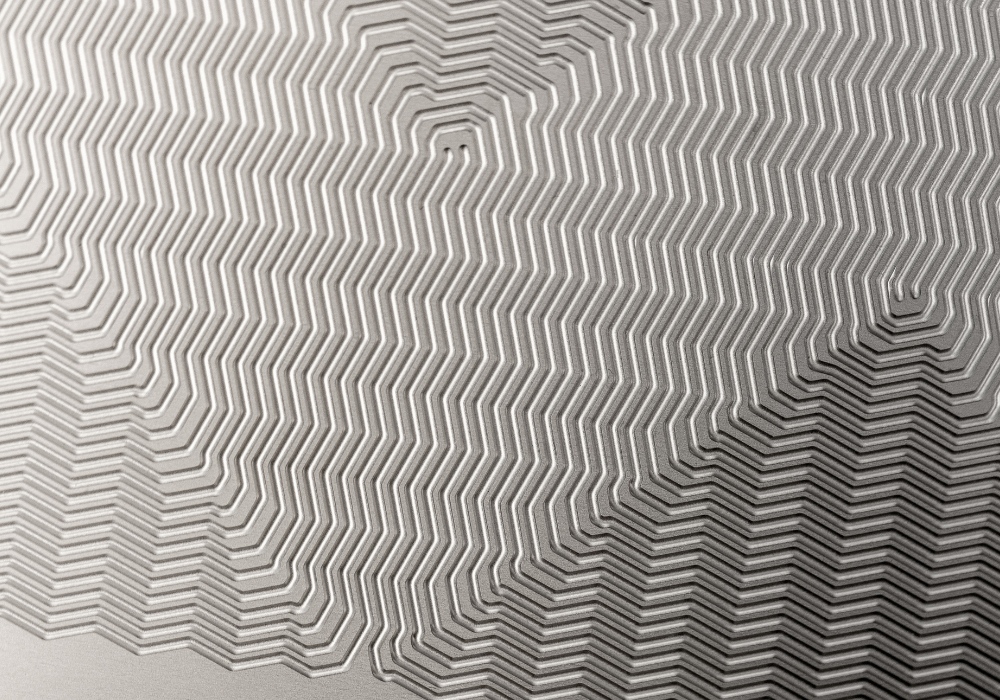

Photochemical etching offers unmatched repeatability and precision, facilitating the creation of microchannels as wide as 0.1mm and as deep as 0.025mm with a consistently high degree of accuracy. This enables more compact and efficient heat transfer whilst reducing the surface area.
Why partner with Precision Micro for the manufacture of PCHE flow plates?
At Precision Micro, we have over 60 years of experience in chemical etching, coupled with more than 30 years of expertise in supplying printed circuit heat exchanger flow plates to leading OEMs. Our production facility, recently enhanced with a significant €2.1 million ($2.3 million) investment into a new state-of-the-art etch room, has been specifically designed to manufacture printed circuit heat exchangers faster and more cost-effectively at higher volumes.
Conclusion
Chemical etching is the key solution for manufacturing printed circuit heat exchanger flow plates, ensuring efficient thermal energy transfer with minimal footprint while preserving material integrity. This cost-effective and time-efficient process, combined with Precision Micro’s expertise in chemical etching and advanced production facility, enables the delivery of high-quality PCHE flow plates whilst reducing time-to-market.
Download our heat exchanger application note to learn more.
Chemical Etching Whitepaper
Learn how chemical etching can overcome the limitations of traditional sheet metal machining technologies.
Download