Chemical etching process step-by-step
What is chemical etching?
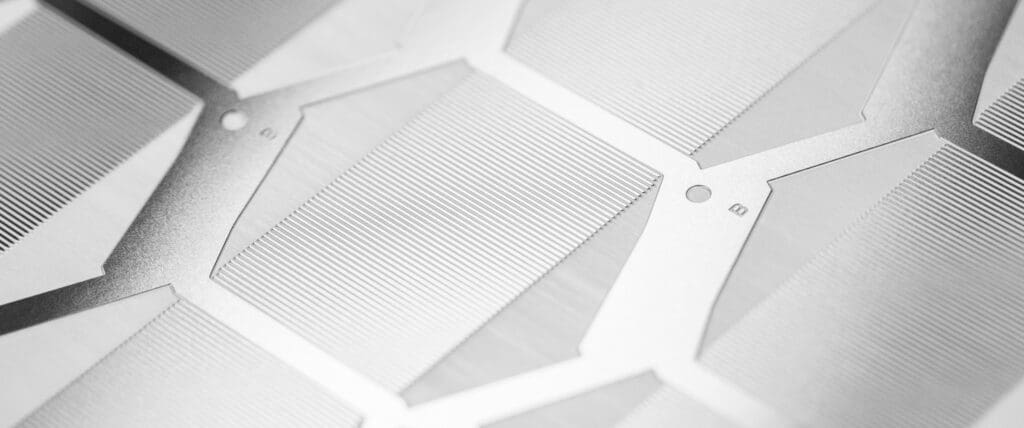
Chemical etching is a machining process that uses chemicals to produce precision components from various metals. The process involves applying a corrosive etchant, typically ferric chloride, to dissolve unwanted metal and achieve the final design.
In this post, we look at chemical etching step by step. For an in-depth guide to the process, download our free chemical etching whitepaper.
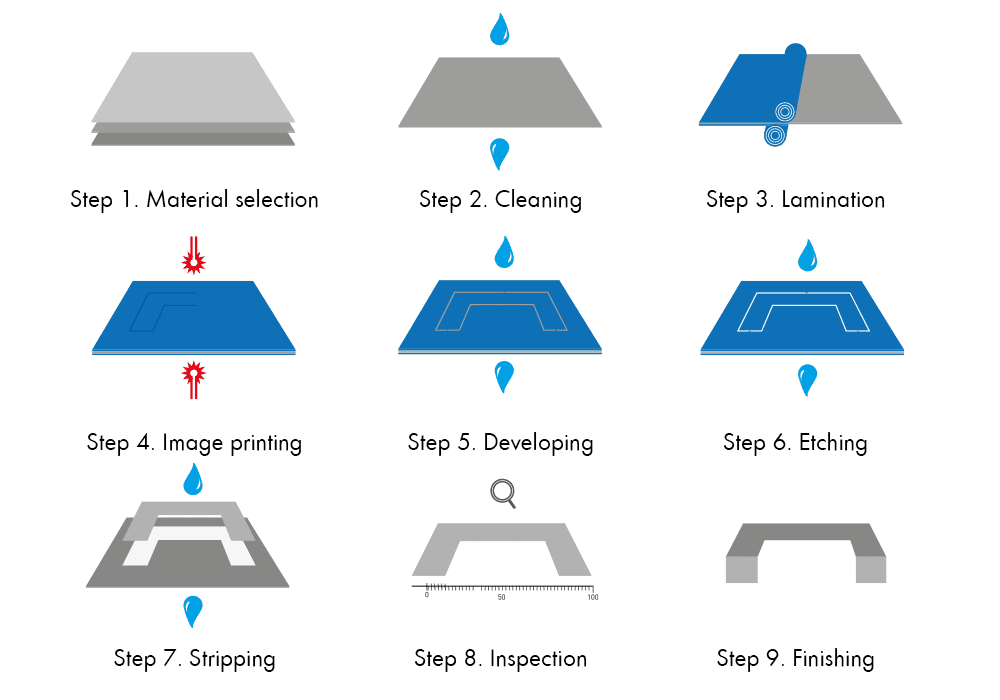
1. Material Selection
The chemical etching process starts with the selection of the required sheet metal, with suitable thicknesses ranging from 0.010 mm to 2.5 mm and sheet sizes up to 600 mm by 1500 mm.
Typical metals include:
2. Pre-clean
Once a metal has been selected, it is chemically cleaned and degreased to remove debris, waxes and rolling oils, all of which could negatively affect the next stage of the process.

3. Lamination
An ultraviolet (UV) light-sensitive photoresist is applied to the sheet. Good adhesion is essential for highly repeatable, blemish-free components. Any issue with the bonding of the laminate could allow the etchant to come into contact with the protected areas of the metal during etching, compromising the finished parts.
4. Printing
The component design is transferred to the photoresist by exposing the sheet to UV light through a photo tool stencil.
5. Developing
The unexposed photoresist is removed, exposing the raw material. The remaining photoresist will protect the sheet part during the etching process.
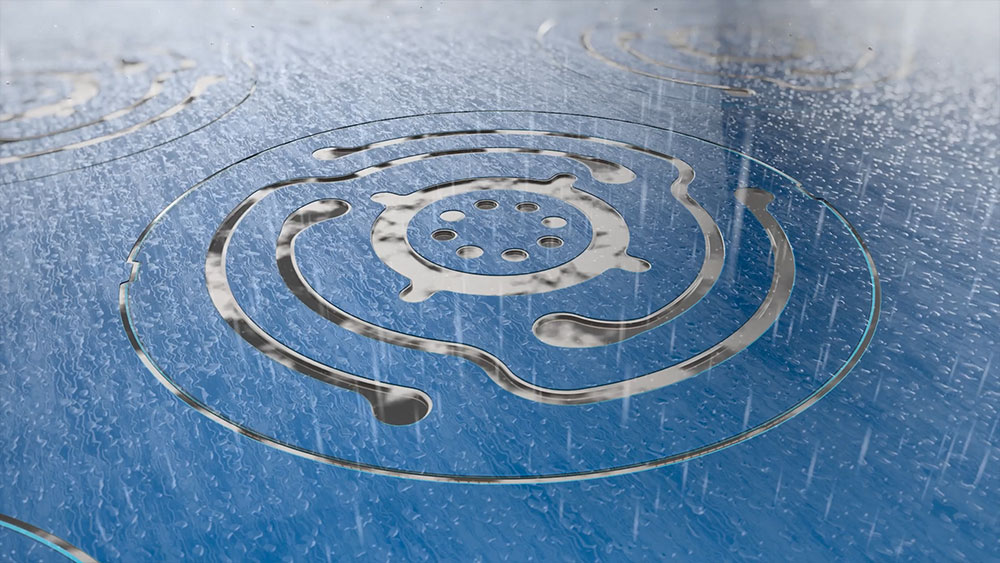

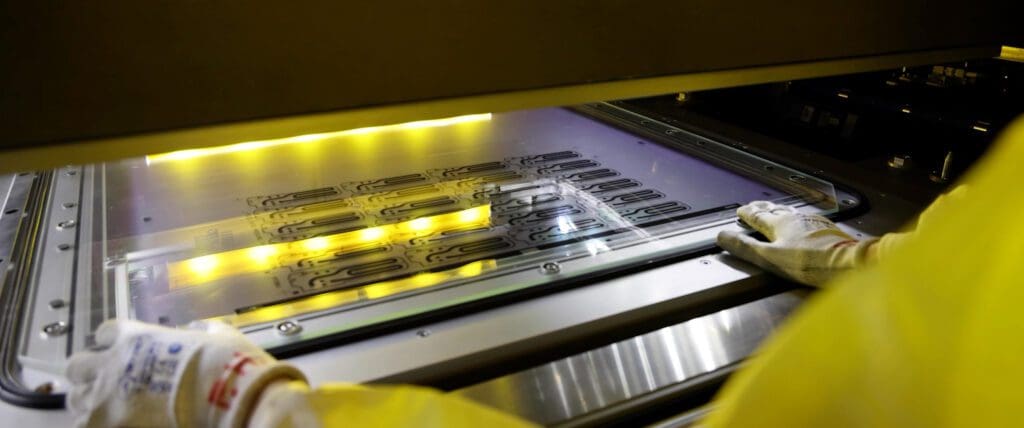
6. Etching
Etchant chemistry, typically ferric chloride, is sprayed onto the developed sheet. The etch-time is determined by skilled technicians taking account of variables such as metal type, grade, thickness and size, all of which affect the end result.
Read our 10 chemical etching FAQs
7. Stripping
The remaining photoresist is removed from the sheet, revealing the final etched components.
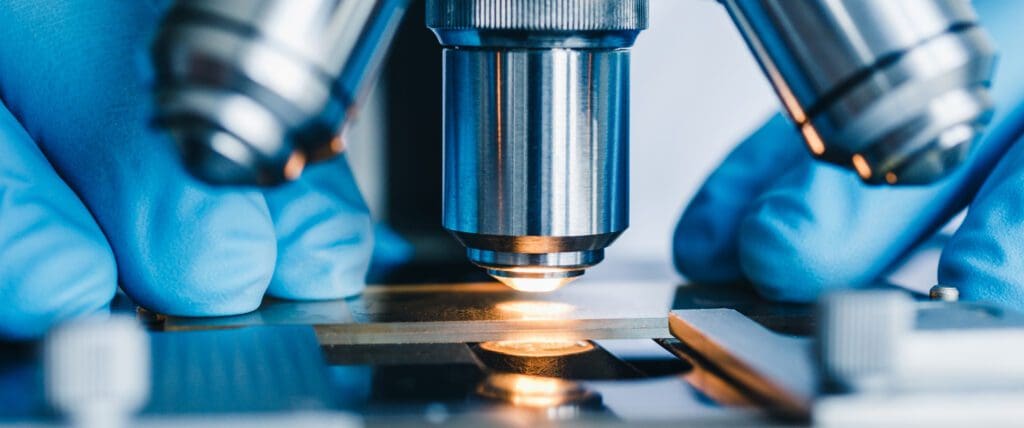
8. Visual and dimensional inspection
The components are visually and dimensionally inspected using state-of-the-art optical inspection equipment.
9. Finishing
If required, etching can be combined with other processes including:
- Plating
- Forming
- Electropolishing
- Passivation
- Heat treatment
- Brazing and diffusion bonding
- Wire EDM
Learn more about Precision Micro’s industry leading chemical etching service.
Chemical Etching Whitepaper
Learn how chemical etching can overcome the limitations of traditional sheet metal machining technologies.
Download